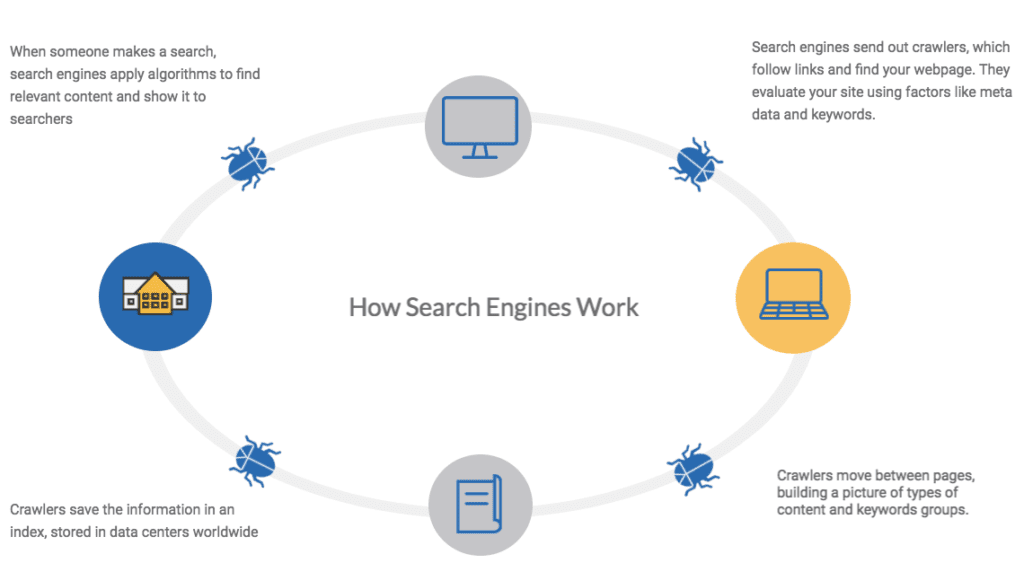
Search engines have become an integral part of our daily lives. We rely on them to instantly find relevant information online with just a few clicks and keystrokes. But what’s actually happening behind that simple search box? How do search engines manage to return pages of on-target results at lightning speed? Let’s explore the technology powering modern search.
Read Also: Why Is SEO Important? (Quick Guide 2024)
Crawling and Indexing The Web
The first critical process in understanding search engines is web crawling and indexing.
Web Crawlers
Also referred to as spiders, web crawlers are automated programs that methodically browse the world wide web by recursively following hyperlinks from site to site. As they traverse this massive network of interconnected sites, the crawlers discover new webpages and content to be indexed by the search engine.
Creating An Index
As these intelligent crawlers explore and scan billions of pages across the internet, the search engine stores key information about each webpage in a massive centralized database index. This includes data like page content, titles, metadata, links, images, files, URLs and more.
Crawling Prioritization
With over 1.7 billion websites now existing, it’s impossible for crawlers to scan the entire web in a comprehensive manner. So search engines rely on complex proprietary algorithms and heuristics to judiciously determine crawling priorities. Factors like site freshness, change frequency, perceived quality and importance of content all impact the order in which pages get crawled and updated.
Processing Search Queries
When you tap out a question or keywords into Google’s familiar search bar and hit enter, several crucial steps rapidly take place under the hood before results appear:
Analyzing Keywords
Powerful query processing software immediately analyzes the specific keywords, phrases and questions you entered to try and determine the true nature of your search intent and the type of information being sought.
Matching to Index
Leveraging the search index cataloging vast data about websites and pages across the web, the engine’s algorithms can then quickly scan and match to discover pages that contain textual content related to your search keywords that might satisfy the user intent.
Ranking Relevant Results
Additional proprietary ranking signals like authority, trust, quality metrics, and user experience help the search engine almost instantly sort and filter the most relevant results to the top to return in the SERPs based on the context of the query.
Showing Results
Mere seconds after you hit search, the engine rapidly analyzes, assesses and ranks pages, then displays the top 10 blue result links deemed most authoritative and relevant to your keywords so you can access the information you want.
Crawling Challenges
Efficient large-scale web crawling faces inherent challenges including:
Scale
The web is unimaginably massive and dynamic – over 1.7 billion interlinked websites and counting, with constant changes happening. Trying to crawl even a considerable fraction thoroughly and in context is practically impossible, requiring very sophisticated prioritization.
Hidden Content
Not all useful metadata, images, videos or other supplemental content is readily visible or accessible to standard web crawlers as they scan. So gaps can occur in what gets indexed, limiting search visibility. Specialized tools can help uncover these hidden areas.
Site Speed
Slow website performance and page load times greatly hinders timely crawling and index refreshing. Speed optimizations are hugely beneficial for allowing more frequent, impactful crawling.
Spam Sites
As search giants battle types of algorithm manipulation, low-quality spammy sites with deliberately manipulative SEO tactics can sometimes fool engines and contaminate rankings integrity if not smartly detected during the crawling process. Identifying and demoting spam protects relevancy.
FAQs
How often do crawlers revisit a site?
Frequency varies based on freshness signals and competition, but on average, search engine web crawlers will revisit most websites about once every 1-2 months in order to recrawl and update the indexed data.
What is indexing?
Indexing refers to the process search engines use to store key data points discovered about webpages by crawlers into a massive, organized searchable database structure allowing lightning-fast queries to match and retrieve pages by relevancy.
How are mobile sites crawled?
The same essential web crawling goals and principles apply in a mobile context, but there is now additional prioritization on responsiveness, page speed, and other mobile-specific usability signals to meet the demands of growing mobile search usage.
Why is SEO important for crawling?
Search engine optimization (SEO) helps structure websites, page content and metadata in an optimal way to be more easily and correctly interpreted, indexed and valued by search engine crawlers to enhance visibility.
How can I get my site indexed faster?
Improving a website’s crawl budget by adding fresh quality content, speed optimizations, efficient site architecture and internal linking helps trigger quicker and repeated indexing by search engines over time.
Conclusion
It’s clear that sophisticated search engine technology relies on a complex interplay of web crawling, indexing, instant query processing, and relevancy ranking algorithms happening behind that little search box we take for granted. Achieving higher visibility in search engine results requires an understanding of how information is discovered, cataloged and matched based on search intent.
By optimizing a website for these automated yet intelligent processes through ongoing SEO best practices, businesses can drive higher organic growth, leads and conversions leveraging the power of search engines. In our digital world, manipulating the science in search is key to online success.